Textbook Question
What would happen to the citric acid cycle if NADH and FADH2 were not reoxidized?
1421
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
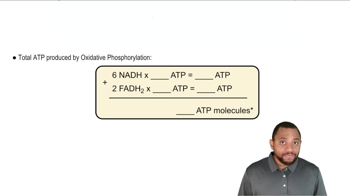

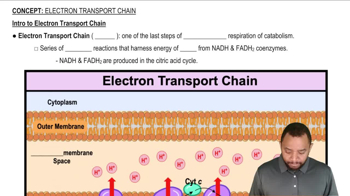
What would happen to the citric acid cycle if NADH and FADH2 were not reoxidized?
What does the term “oxidative phosphorylation” mean? What is substrate-level phosphorylation? Are these processes the same? Explain.
In oxidative phosphorylation, what is oxidized and what is phosphorylated?
What supplies the energy to drive oxidative phosphorylation?
Why must the breakdown of molecules for energy in the body occur in several steps, rather than in one step?
With what class of enzymes are the coenzymes NAD+ and FAD associated?