Lactate can be converted into pyruvate by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase and the coenzyme NAD+. Write the reaction in the standard biochemical format, using a curved arrow to show the involvement of NAD+.
Ch.22 Carbohydrate Metabolism

Chapter 22, Problem 61
Name the anabolic pathway for making glucose.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that an anabolic pathway is a metabolic process that builds larger molecules from smaller ones, requiring energy input.
Recognize that the process of making glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors is called gluconeogenesis.
Recall that gluconeogenesis primarily occurs in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys.
Note that gluconeogenesis uses substrates such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, and certain amino acids to synthesize glucose.
Understand that gluconeogenesis is essentially the reverse of glycolysis, but it bypasses the irreversible steps of glycolysis using specific enzymes like pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis is the metabolic pathway through which organisms synthesize glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. This process primarily occurs in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidneys. It is crucial during periods of fasting or intense exercise when glucose levels are low, allowing the body to maintain energy homeostasis.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gluconeogenesis Example 2
Anabolic Pathways
Anabolic pathways are metabolic routes that construct molecules from smaller units, requiring energy input. These pathways are essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of cellular structures. In the context of gluconeogenesis, it represents the synthesis of glucose, contrasting with catabolic pathways that break down molecules to release energy.
Recommended video:
Guided course
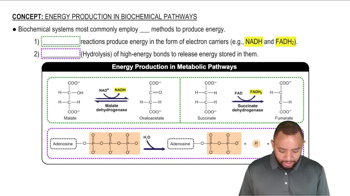
Energy Production In Biochemical Pathways Concept 1
Substrates of Gluconeogenesis
The substrates of gluconeogenesis include lactate, glycerol, and certain amino acids, which serve as building blocks for glucose synthesis. These substrates are converted through a series of enzymatic reactions, ultimately leading to the formation of glucose. Understanding these substrates is vital for grasping how the body generates glucose from various sources during metabolic stress.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gluconeogenesis Example 2
Related Practice
Textbook Question
894
views
Textbook Question
Differentiate between blood sugar levels and resulting symptoms in hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
749
views
Textbook Question
Why does glycogenolysis use fewer steps than the reverse process, glycogenesis? Which process uses less energy?
1137
views
Textbook Question
Name the two molecules that serve as starting materials for glucose synthesis.
819
views
Textbook Question
How many steps in gluconeogenesis are not the exact reversal of the steps in glycolysis? What kind of conversion of substrate to product does each involve? What is the common theme in each of these reactions?
724
views
Textbook Question
Explain why the Cori cycle is necessary and when your cells would use this cycle.
681
views
