Textbook Question
How many moles of ATP are produced by phosphorylation in the following?
a. Glycolysis of 1 mol of glucose
734
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
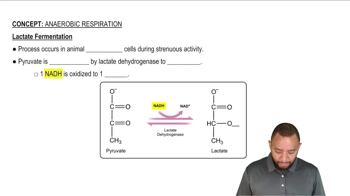


How many moles of ATP are produced by phosphorylation in the following?
a. Glycolysis of 1 mol of glucose
How many moles of ATP are produced by phosphorylation in the following?
b. Aerobic conversion of 1 mol of pyruvate to 1 mol of acetyl-CoA
How many moles of ATP are produced by phosphorylation in the following?
c. Catabolism of 1 mol of acetyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle
Differentiate between blood sugar levels and resulting symptoms in hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Why does glycogenolysis use fewer steps than the reverse process, glycogenesis? Which process uses less energy?
Name the anabolic pathway for making glucose.