Glucose 6-phosphate is in a pivotal position in metabolism. Depending on conditions, glucose 6-phosphate follows one of several pathways. Under what conditions do the following occur?
b. Hydrolysis to free glucose

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Glucose 6-phosphate is in a pivotal position in metabolism. Depending on conditions, glucose 6-phosphate follows one of several pathways. Under what conditions do the following occur?
b. Hydrolysis to free glucose
Glucose 6-phosphate is in a pivotal position in metabolism. Depending on conditions, glucose 6-phosphate follows one of several pathways. Under what conditions do the following occur?
d. Glycogenesis
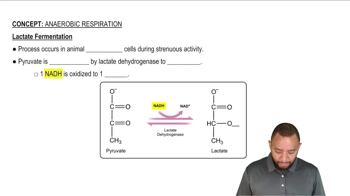
Outline the conditions that direct pyruvate toward the following:
b. Conversion to ethanol and CO2
In what tissues or organisms is each pathway present?
Outline the conditions that direct pyruvate toward the following:
d. Glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis)
In what tissues or organisms is each pathway present?
Name the molecules used for gluconeogenesis. What are the sources of these molecules? Under what conditions would gluconeogenesis occur?
Fatty acids from stored triacylglycerols (fat) are not available for gluconeogenesis. Speculate why we do not have the enzymes to directly convert fatty acids into glucose. Plants (especially seeds) do have enzymes to convert fatty acids into carbohydrates. Why are they so lucky?