Textbook Question
What are the major monosaccharide products produced by digestion of carbohydrates?
747
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
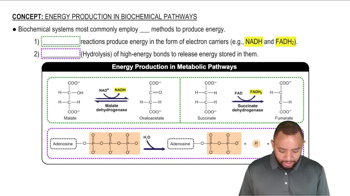
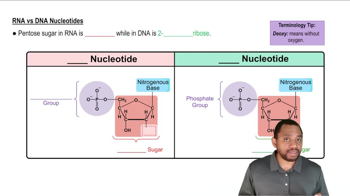
What are the major monosaccharide products produced by digestion of carbohydrates?
What are the products of digestion of proteins, triacylglycerols, maltose, sucrose, lactose, and starch?
What three products are formed from pyruvate under aerobic, anaerobic, and fermentation conditions?
Which cells, liver, muscle, or brain, use the following pathways?
a. Glycolysis
Which cells, liver, muscle, or brain, use the following pathways?
b. Gluconeogenesis
Which glycolysis reactions are catalyzed by the following enzymes?
a. Pyruvate kinase