As noted earlier (Section 22.3), he first step in glycolysis, which occurs within cells, is phosphorylation of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate. Why does this step prevent passive diffusion of glucose back out of the cell?

Draw an 18-carbon saturated fatty acid. Is this a “straight-chain” molecule or a “bent” molecule?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Saturated Fatty Acids
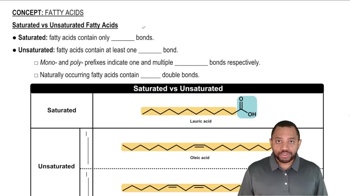
Molecular Structure

Straight-Chain vs. Bent Molecules

Complete hydrogenation of triacylglycerol C in Problem 23.20 yields a triacylglycerol of what fatty acid composition? Would the hydrogenation product of triacylglycerol C be more like the hydrogenation product of triacylglycerol A or B? Explain.
A membrane lipid was isolated and completely hydrolyzed. The following products were detected: ethanolamine, phosphate, glycerol, palmitic acid, and oleic acid. Propose a structure for this membrane lipid, and name the family to which it belongs.
Draw an 18-carbon unsaturated fatty acid that contains two carbon–carbon double bonds, one on carbon 6 and one on carbon 9 (count starting with the carboxyl carbon). Is this a “straight-chain” molecule or a “bent” molecule?
Are the carbon–carbon double bonds in naturally occurring fatty acids primarily cis or trans?
Which of these fatty acids has the lower melting point? Explain why.
a. Linoleic acid
b. Stearic acid
