How many rounds of the lipogenesis cycle are needed to synthesize stearic acid, C17H35COOH?
Ch.24 Lipid Metabolism

Chapter 24, Problem 68
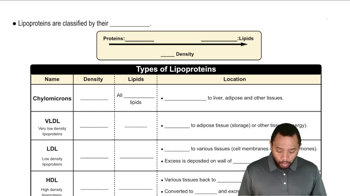
Lipoproteins that transport lipids from the diet are described as exogenous. Those that transport lipids produced in metabolic pathways are described as endogenous. Which of the following lipoproteins transports exogenous lipids and which transports endogenous lipids?
a. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
b. Chylomicrons
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the key terms: Exogenous lipids are those obtained from the diet, while endogenous lipids are those synthesized within the body through metabolic pathways.
Recall the function of chylomicrons: Chylomicrons are lipoproteins that transport dietary (exogenous) lipids, such as triglycerides, from the intestines to other tissues in the body.
Recall the function of low-density lipoprotein (LDL): LDL is a lipoprotein that primarily transports cholesterol, which is synthesized in the liver (endogenous), to peripheral tissues.
Classify chylomicrons: Based on their role in transporting dietary lipids, chylomicrons are responsible for transporting exogenous lipids.
Classify LDL: Based on its role in transporting cholesterol produced in the body, LDL is responsible for transporting endogenous lipids.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lipoproteins
Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of lipids and proteins that transport fats through the bloodstream. They vary in density and function, with different types responsible for carrying either dietary lipids (exogenous) or lipids synthesized by the body (endogenous). Understanding the role of lipoproteins is crucial for grasping how lipids are distributed and utilized in the body.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Lipoproteins for Transport Concept 2
Exogenous vs. Endogenous Lipids
Exogenous lipids are those derived from dietary sources, primarily transported by chylomicrons, which are formed in the intestines after fat consumption. In contrast, endogenous lipids are produced by the liver and transported by lipoproteins such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL). This distinction is essential for understanding lipid metabolism and the implications for health and disease.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro to Lipids Example 1
Chylomicrons and LDL
Chylomicrons are a type of lipoprotein that specifically transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other tissues, making them key players in the exogenous lipid transport pathway. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL), on the other hand, is primarily responsible for carrying cholesterol and other lipids from the liver to peripheral tissues, representing the endogenous lipid transport pathway. Recognizing the functions of these lipoproteins helps in understanding their roles in cardiovascular health.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lipoproteins for Transport Concept 2
Related Practice
Textbook Question
691
views
Textbook Question
Consuming too many carbohydrates causes deposition of fats in adipose tissue. How does this happen?
612
views
Textbook Question
Why are extra calories consumed as carbohydrates stored as fat and not as glycogen?
1021
views
Textbook Question
High blood-cholesterol levels are dangerous because of their correlation with atherosclerosis and consequent heart attacks and strokes. Is it possible to eliminate all cholesterol from the bloodstream by having a diet that includes no cholesterol? Is it desirable to have no cholesterol at all in your body? Explain your answer.
618
views
Textbook Question
A low-fat diet of pasta, bread, beer, and soda can easily lead to an increase in weight. The increase is stored triacylglycerols in adipocytes. Explain the weight increase and why the excess carbohydrate is stored as fat.
709
views
