Textbook Question
Write the equation for the hydrolysis of a triacylglycerol composed of stearic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid by pancreatic lipase.
557
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

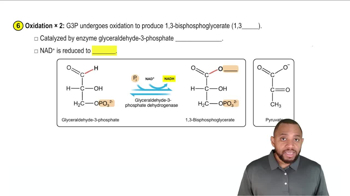
Write the equation for the hydrolysis of a triacylglycerol composed of stearic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid by pancreatic lipase.
What is the origin of the triacylglycerols transported by very low-density lipoproteins?
How is cholesterol transported around the body? When it leaves the liver, what is its destination and use?
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA result from catabolism of 1 molecule of glyceryl trilaurate?
Why is the stepwise oxidation of fatty acids called β oxidation?
How many moles of ATP are produced by the complete oxidation of 1 mol of myristic acid?