Textbook Question
What citric acid cycle intermediates are precursors to amino acids?
1106
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
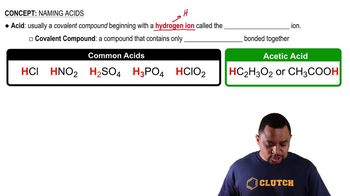

What citric acid cycle intermediates are precursors to amino acids?
What is the structure of the ⍺-keto acid formed from transamination of the following amino acids?
a. Glutamic acid
In general, how does oxidative deamination differ from transamination?
What other product is formed in oxidative deamination besides an ⍺-keto acid?
Why does the body convert NH4+ to urea for excretion?
From what two amino acids do the nitrogens in urea arise?
<IMAGE>