Back
BackProblem 1
Classify each defense as either first-line, second-line cellular, or second-line molecular:
Inflammation
Neutrophils
Skin
Antimicrobial peptides
Lysozyme
Stomach acid
Eosinophils
Fever
Complement proteins
Mucus
Iron-binding proteins
Phagocytosis
Problem 2
Pick which statements are true, then correct all false statements, so they are also true.
a. Redness, pain, fever, and swelling characterize inflammation.
b. Granulocytes include monocytes and lymphocytes.
c. Pyrogens induce fever.
d. Adaptive and innate immune responses are completely independent from one another.
e. The innate immune responses occur faster than adaptive responses.
f. Monocytes are highly phagocytic cells.
g. Complement cascades share the same outcomes: opsonization, cytolysis, and fever.
Problem 3
Which of the following would most directly reduce fever? Select all that apply.
a. Limiting the number of circulating white blood cells
b. Reducing eicosanoid production
c. Inhibiting pyrogenic cytokines
d. Stimulating the action of prostaglandins
e. Administering antihistamines
Problem 4
Which of the following would you expect to see in acute infection by a Gram-negative bacterium? Select all that apply.
a. Pyrexia
b. Decreased lymphocytes
c. Neutrophilic lymphocytosis
d. Decreased monocytes
e. Increased release of pro-inflammatory cytokines
Problem 5
Which of the following would you expect to see increased in circulation in a patient suffering from allergies? Select all that apply.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Problem 6
The ____________ cascade of complement activation is initiated by antibodies. In contrast, the ____________ cascade is activated by a direct interaction with complement proteins, and the ____________ cascade is activated by MBL associating with a pathogen.
Problem 7
Which of the following would you not expect to see in the first stage of inflammation?
a. Histamine
b. Kinins
c. Macrophages
d. Increased blood vessel permeability
e. Eicosanoids
Problem 8
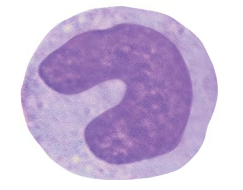
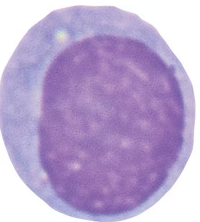
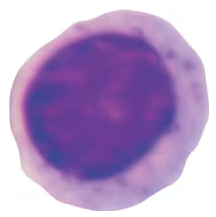
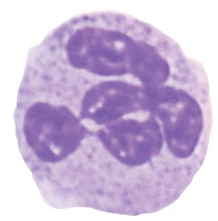
Label the following as granulocytes or agranulocytes and classify them as innate or adaptive cellular responders.
Basophil
Monocyte
Macrophage
Lymphocyte
Neutrophil
Eosinophil
Mast cell
NK cell
T cell
Problem 9
Make a Venn diagram to compare and contrast innate and adaptive immunity.
Problem 10
Which of the following would be the most likely immediate consequence of an aseptic tissue injury?
a. Monocytosis
b. Complement activation
c. Eosinophilia
d. Fever
e. Inflammation
Problem 11
Which of the following is not a feature of innate immunity?
a. Better protection upon later exposure to a given pathogen
b. Recognition of diverse pathogens
c. Discrimination between self and foreign
d. Killing of identified invaders
e. Stimulation of adaptive immunity
Problem 11
Which of the following are considered cytokines? Select all that apply.
a. Eicosanoids
b. TNF- α
c. Interferon β
d. Histamine
e. Chemokines
Problem 12
____________ are innate molecular defenses that collectively limit free iron in the blood. Examples of these factors in humans include ____________, ____________, ____________, and ____________.
Problem 13
Which would be expected to contribute to chronic inflammation? Select all that apply.
a. A reduced innate defense
b. Fever
c. Persistent tissue injury
d. Glucocorticosteroids
e. Antihistamines
Problem 15
Label the following as either primary or secondary lymphoid tissues:Spleen, lymph node, adenoids, thymus, tonsils, bone marrow
Problem 16
Why are vascular changes in early inflammation considered central to generating inflammation’s cardinal signs?
Problem 17
Which of the following is false regarding histamine?
a. Histamine is a vasodilator
b. Histamine increases vascular permeability
c. Histamine is a pro-inflammatory factor
d. Histamine is a pyrogen
e. Histamine is released by leukocytes
Problem 17.10a
All of the following defend the eyes EXCEPT:
a. tears.
b. lysozyme.
c. several corneal epithelial layers.
d. a hard external layer encasing the entire eyeball, including the cornea.
e. lactoferrin.
Problem 18
Why is innate immunity considered a generalized defense?
Problem 19
Which of the following shows a correct chronological order of events in inflammation?
a. Neutrophil recruitment, macrophage recruitment, vascular changes, resolution
b. Vascular changes, resolution, neutrophil recruitment, macrophage recruitment
c. Vascular changes, macrophage recruitment, neutrophil recruitment, resolution
d. Vascular changes, macrophage recruitment, resolution, neutrophil recruitment
e. Vascular changes, neutrophil recruitment, macrophage recruitment, resolution
Problem 20
Select all the false statements about fever.
a. It is generated by pyrogens
b. It is an innate immune defense
c. It is accompanied by a decrease in metabolism
d. It can be reduced by anti-inflammatory drugs
e. It can accompany inflammation
Problem 21
Which of the following is a chemical defense found in tears? Select all that apply.
a. Water
b. Lysozyme
c. Antimicrobial peptides
d. Neutrophils
Problem 22
Which of the following are formed elements of the blood? Select all that apply.
a. Platelet
b. Leukocyte
c. Plasma
d. Erythrocyte
e. Complement proteins
Problem 23
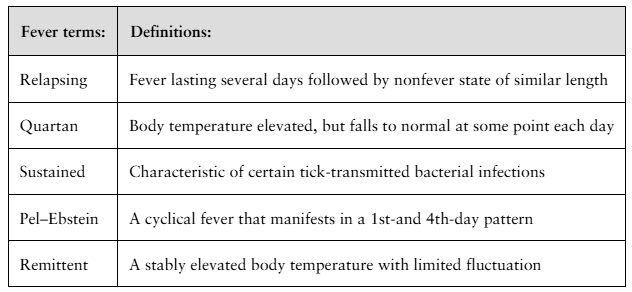
Match the following fever terms to their proper definition; not all definitions will be used.