Textbook Question
In Exercises 17–30, determine the amplitude, period, and phase shift of each function. Then graph one period of the function.y = 1/2 sin(x + π/2)
682
views

 Blitzer 3rd Edition
Blitzer 3rd Edition Ch. 2 - Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions; Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Ch. 2 - Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions; Inverse Trigonometric Functions Problem 25
Problem 25 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
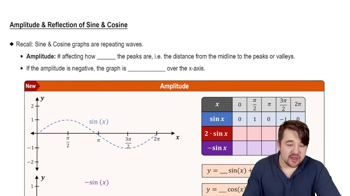

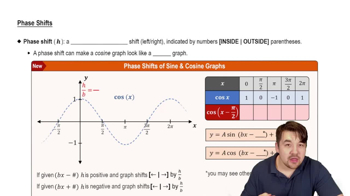
Determine the amplitude, period, and phase shift of each function. Then graph one period of the function.
y = 1/2 sin(x + π)
Use each graph to obtain the graph of the corresponding reciprocal function, cosecant or secant. Give the equation of the function for the graph that you obtain.
<IMAGE>