The sites where the motor nerve impulse is transmitted from the nerve endings to the skeletal muscle cell membranes are the
a. neuromuscular junctions
b. sarcomeres
c. myofilaments
d. Z discs

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
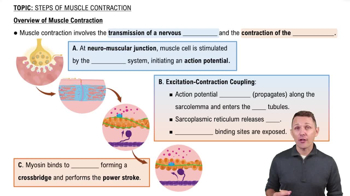


The sites where the motor nerve impulse is transmitted from the nerve endings to the skeletal muscle cell membranes are the
a. neuromuscular junctions
b. sarcomeres
c. myofilaments
d. Z discs
Contraction elicited by a single brief stimulus is called:
a. A twitch
b. Temporal summation
c. Multiple motor unit summation
d. Fused tetanus
A smooth, sustained contraction resulting from very rapid stimulation of the muscle, in which no evidence of relaxation is seen, is called:
a. A twitch
b. Temporal summation
c. Multiple motor unit summation
d. Fused tetanus
During muscle contraction, ATP is provided by:
a. a coupled reaction of creatine phosphate with ADP
b. aerobic respiration of glucose, and
c. anaerobic glycolysis.
______ (1) Which provides ATP fastest?
______ (2) Which does (do) not require that oxygen be available?
______ (3) Which provides the highest yield of ATP per glucose molecule?
______ (4) Which results in the formation of lactic acid?
______ (5) Which has carbon dioxide and water products?
______ (6) Which is most important in endurance sports?
The neurotransmitter released by somatic motor neurons is:
a. Acetylcholine
b. Acetylcholinesterase
c. Norepinephrine
The ions that enter the skeletal muscle cell during the generation of an action potential are
a. Calcium ions
b. Chloride ions
c. Sodium ions
d. Potassium ions