Textbook Question
A substance moving across a membrane against a concentration gradient is moving by ________.
a. Passive transport
b. Osmosis
c. Facilitated diffusion
d. Active transport
e. Diffusion
2506
views

 Belk, Maier 6th Edition
Belk, Maier 6th Edition Ch. 3 - Is It Possible to Supplement Your Way to Better Performance and Health?
Ch. 3 - Is It Possible to Supplement Your Way to Better Performance and Health? Problem 10
Problem 10 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

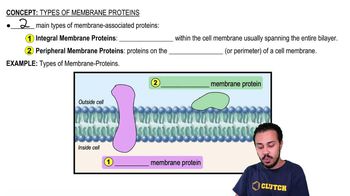

A substance moving across a membrane against a concentration gradient is moving by ________.
a. Passive transport
b. Osmosis
c. Facilitated diffusion
d. Active transport
e. Diffusion
A cell that is placed in salty seawater will ________.
a. Take sodium and chloride ions in by diffusion.
b. Move water out of the cell by active transport.
c. Use facilitated diffusion to break apart the sodium and chloride ions.
d. Lose water to the outside of the cell via osmosis.
Which of the following forms of membrane transport require specific membrane proteins?
a. Diffusion
b. Exocytosis
c. Facilitated diffusion
d. Active transport
e. Facilitated diffusion and active transport