Back
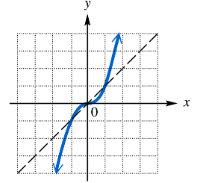
BackProblem 11
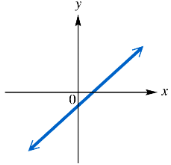
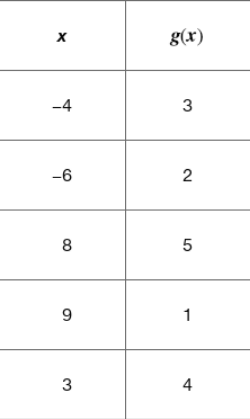
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one.
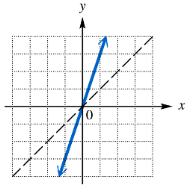
Problem 13
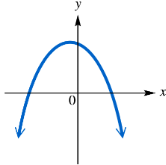
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one.
Problem 15
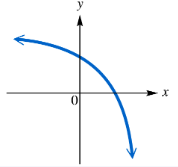
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one.
Problem 17
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = 2x - 8
Problem 20
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = -√(100 - x2)
Problem 21
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = 2x3 - 1
Problem 23
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = -1 / x+2
Problem 25
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = x+4 / x-3
Problem 27
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = 2(x+1)2 - 6
Problem 29
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = -(√x)+5
Problem 31
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = 5|x+2|
Problem 33
Determine whether each function graphed or defined is one-to-one. y = ∛(x+1) - 3
Problem 41
Use the definition of inverses to determine whether ƒ and g are inverses. f(x) = x+1/x-2, g(x) = 2x+1/x-1
Problem 43
Use the definition of inverses to determine whether ƒ and g are inverses. f(x) = 2/(x+6), g(x) = (6x+2)/x
Problem 45
Use the definition of inverses to determine whether ƒ and g are inverses. f(x) = x2+3, x≥0; g(x) = √x-3, x≥3
Problem 47
Determine whether the given functions are inverses.
Problem 49
Determine whether the given functions are inverses. ƒ= {(2,5), (3,5), (4,5)}; g = {(5,2)}
Problem 52
Find the inverse of each function that is one-to-one. {(3,-1), (5,0), (0,5), (4, 2/3)}
Problem 53
Find the inverse of each function that is one-to-one. {(1, -3), (2, -7), (4, -3), (5, -5)}
Problem 55
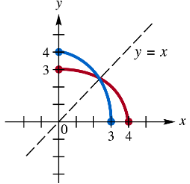
Determine whether each pair of functions graphed are inverses.
Problem 56
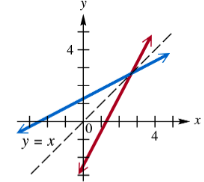
Determine whether each pair of functions graphed are inverses.
Problem 57
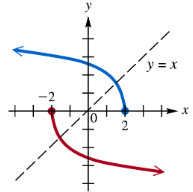
Determine whether each pair of functions graphed are inverses.
Problem 77
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 79
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 81
Graph the inverse of each one-to-one function.
Problem 6
Fill in the blank(s) to correctly complete each sentence. The graph of ƒ(x) = -(1/3)x+4-5 is that of ƒ(x) = (1/3)x reflected across the ______ -axis, translated to the left ______ units and down _______ units.
Problem 13
For ƒ(x) = 3x and g(x)= (1/4)x find each of the following. Round answers to the nearest thousandth as needed. ƒ(-2)
Problem 15
For ƒ(x) = 3x and g(x)= (1/4)x find each of the following. Round answers to the nearest thousandth as needed. g(2)
Problem 20
For ƒ(x) = 3x and g(x)= (1/4)x find each of the following. Round answers to the nearest thousandth as needed. ƒ(-5/2)
Problem 21
For ƒ(x) = 3x and g(x)= (1/4)x find each of the following. Round answers to the nearest thousandth as needed. g(3/2)