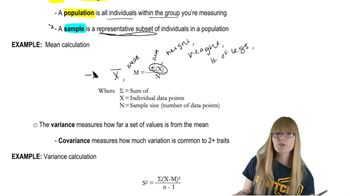
In pea plants, the appearance of flowers along the main stem is a dominant phenotype called 'axial' and is controlled by an allele T. The recessive phenotype, produced by an allele t, has flowers only at the end of the stem and is called 'terminal.' Pod form displays a dominant phenotype, 'inflated,' controlled by an allele C, and a recessive 'constricted' form, produced by the c allele. A cross is made between a pure-breeding axial, constricted plant and a plant that is pure-breeding terminal, inflated.
If an F₁ plant from the initial cross described above is crossed with a plant that is terminal, constricted, what is the expected distribution among the resulting progeny?