Thinking back to the discussion of gain-of-function and loss-of-function mutations, explain why gain-of-function mutations are often dominant and why loss-of-function mutations are often recessive. Give an example of a type of gain-of-function mutation that is dominant and of a loss-of-function mutation that is recessive.

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination
Ch. 11 - Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Homologous Recombination Problem 40c
Problem 40cCommon baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is normally grown at 37°C, but it will grow actively at temperatures down to approximately 25°C. A haploid culture of wild-type yeast is mutagenized with EMS. Cells from the mutagenized culture are spread on a complete-medium plate and grown at 25°C. Six colonies (1 to 6) are selected from the original complete-medium plate and transferred to two fresh complete-medium plates. The new complete plates (shown) are grown at 25°C and 37°C. Four replica plates are made onto minimal medium or minimal plus adenine from the 25°C complete-medium plate. The new plates are grown at either 25°C or 37°C and the growth results are shown.
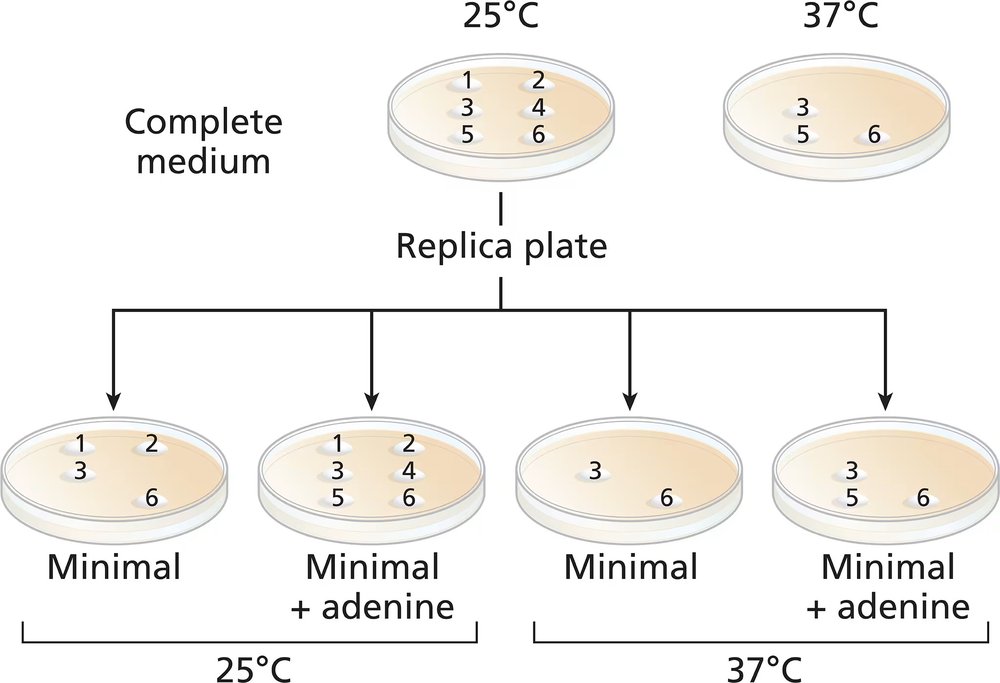
What can you say about colony 4?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Haploidy and Mutagenesis

Temperature Effects on Yeast Growth

Minimal Medium and Nutritional Requirements

Common baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is normally grown at 37°C, but it will grow actively at temperatures down to approximately 25°C. A haploid culture of wild-type yeast is mutagenized with EMS. Cells from the mutagenized culture are spread on a complete-medium plate and grown at 25°C. Six colonies (1 to 6) are selected from the original complete-medium plate and transferred to two fresh complete-medium plates. The new complete plates (shown) are grown at 25°C and 37°C. Four replica plates are made onto minimal medium or minimal plus adenine from the 25°C complete-medium plate. The new plates are grown at either 25°C or 37°C and the growth results are shown.
Which colonies are prototrophic and which are auxotrophic? What growth information is used to make these determinations?
Common baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is normally grown at 37°C, but it will grow actively at temperatures down to approximately 25°C. A haploid culture of wild-type yeast is mutagenized with EMS. Cells from the mutagenized culture are spread on a complete-medium plate and grown at 25°C. Six colonies (1 to 6) are selected from the original complete-medium plate and transferred to two fresh complete-medium plates. The new complete plates (shown) are grown at 25°C and 37°C. Four replica plates are made onto minimal medium or minimal plus adenine from the 25°C complete-medium plate. The new plates are grown at either 25°C or 37°C and the growth results are shown.
Classify the nature of the mutations in colonies 1, 2, and 5.
The two gels illustrated contain dideoxynucleotide DNA-sequencing information for a wild-type segment and mutant segment of DNA corresponding to the N-terminal end of a protein. The start codon and the next five codons are sequenced.
Write the DNA sequence of both alleles, including strand polarity.
The two gels illustrated contain dideoxynucleotide DNA-sequencing information for a wild-type segment and mutant segment of DNA corresponding to the N-terminal end of a protein. The start codon and the next five codons are sequenced.
Identify the template and nontemplate strands of DNA.
The two gels illustrated contain dideoxynucleotide DNA-sequencing information for a wild-type segment and mutant segment of DNA corresponding to the N-terminal end of a protein. The start codon and the next five codons are sequenced.
Write out the mRNA sequences encoded by each template strand, and underline the start codons.