You have identified a 0.80-kb cDNA clone that contains the entire coding sequence of the Arabidopsis gene CRABS CLAW. In the construction of the cDNA library, linkers with EcoRI sites were added to each end of the cDNA, and the cDNA was inserted into the EcoRI site of the MCS of the vector shown in the accompanying figure. You perform digests on the CRABS CLAW cDNA clone with restriction enzymes and obtain the following results. Can you determine the orientation of the cDNA clone with respect to the restriction enzyme sites in the vector? The restriction enzyme sites listed in the dark blue region are found only in the MCS of the vector.

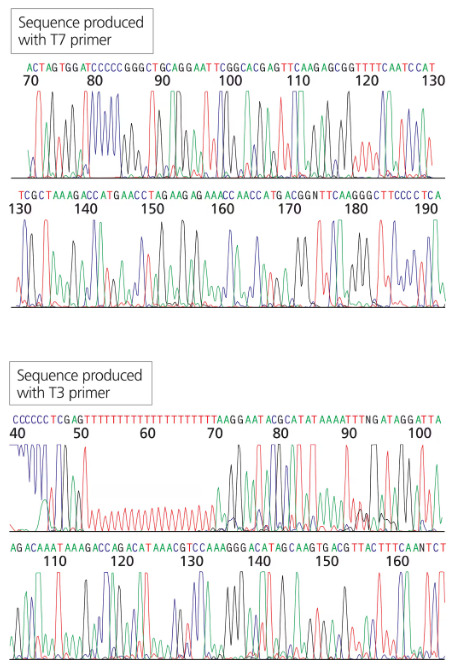
You have isolated another cDNA clone of the CRABS CLAW gene from a cDNA library. The cDNA was directionally cloned using the EcoRI and XhoI sites. You sequence the recombinant plasmid using primers complementary to the T7 and T3 promoter sites flanking the MCS. The first 30 to 60 bases of sequence are usually discarded since they tend to contain errors.
Can you identify the start of the coding region in the end of the gene? What does the sequence preceding the start codon represent?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
cDNA Cloning

Start Codon and Coding Region

5' Untranslated Region (5' UTR)

You have isolated another cDNA clone of the CRABS CLAW gene from a cDNA library. The cDNA was directionally cloned using the EcoRI and XhoI sites. You sequence the recombinant plasmid using primers complementary to the T7 and T3 promoter sites flanking the MCS. The first 30 to 60 bases of sequence are usually discarded since they tend to contain errors.
Will the long stretch of T residues in the T3 sequence exist in the genomic sequence of the gene?
You have isolated another cDNA clone of the CRABS CLAW gene from a cDNA library.. The cDNA was directionally cloned using the EcoRI and XhoI sites. You sequence the recombinant plasmid using primers complementary to the T7 and T3 promoter sites flanking the MCS. The first 30 to 60 bases of sequence are usually discarded since they tend to contain errors.
Can you identify which sequence portions are derived from the vector (specifically the MCS) and which are derived from the cDNA clone?
You have identified five genes in S. cerevisiae that are induced when the yeast are grown in a high-salt (NaCl) medium. To study the potential roles of these genes in acclimation to growth in high-salt conditions, you wish to examine the phenotypes of loss- and gain-of-function alleles of each. How will you do this?
You have identified five genes in S. cerevisiae that are induced when the yeast are grown in a high-salt (NaCl) medium. To study the potential roles of these genes in acclimation to growth in high-salt conditions, you wish to examine the phenotypes of loss- and gain-of-function alleles of each. How would your answer differ if you were working with tomato plants instead of yeast?
You have generated three transgenic lines of maize that are resistant to the European corn borer, a significant pest in many regions of the world. The transgenic lines (T₁ in the accompanying table) were created using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation with a T-DNA having two genes, the first being a gene conferring resistance to the corn borer and the second being a gene conferring resistance to a herbicide that you used as a selectable marker to obtain your transgenic plants. You crossed each of the lines to a wild-type maize plant and also generated a T2 population by self-fertilization of the T1 plant. The following segregation results were observed (herbicide resistant : herbicide sensitive):
Explain these segregation ratios.
