A substantial fraction of almost every genome sequenced consists of genes that have no known function and that do not have sequence similarity to any genes with known function. Describe two approaches to ascertaining the biological role of these genes in S. cerevisiae.

 Sanders 3rd Edition
Sanders 3rd Edition Ch. 16 - Genomics: Genetics from a Whole-Genome Perspective
Ch. 16 - Genomics: Genetics from a Whole-Genome Perspective Problem 24
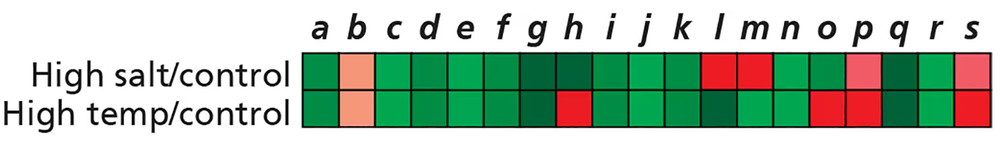
Problem 24You are studying similarities and differences in how organisms respond to high salt concentrations and high temperatures. You begin your investigation by using microarrays to compare gene expression patterns of S. cerevisiae in normal growth conditions, in high salt concentrations, and at high temperatures. The results are shown here, with the values of red and green representing the extent of increase and decrease, respectively, of expression for genes a–s in the experimental conditions versus the control (normal growth) conditions. What is the first step you will take to analyze your data?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Microarrays

Gene Expression Analysis

Data Normalization

A substantial fraction of almost every genome sequenced consists of genes that have no known function and that do not have sequence similarity to any genes with known function. How would your approach change if the genes of unknown function were in the human genome?
In the globin gene family (shown in the below diagram), which pair of genes would exhibit a higher level of sequence similarity, the human δ-globin and human β-globin genes or the human β-globin and chimpanzee β-globin genes? Can you explain your answer in terms of the timing of gene duplications?
In conducting the study described in Problem 24, you have noted that a set of S. cerevisiae genes are repressed when yeast are grown under high-salt conditions. How might you approach this question if genome sequences for the related Saccharomyces species S. paradoxus, S. mikatae, and S. bayanus were also available?
PEG10 (paternally expressed gene 10) is a paternally expressed gene (meaning only the paternal allele is expressed) that has an essential role in the formation of the placenta of the mouse. In the mouse genome, the PEG10 gene is flanked by the SGCE and PPP1R9A genes. To study the origin of PEG10, you examine syntenic regions spanning the SGCE and PPP1R9A loci in the genomes of several vertebrates, and you note that the PEG10 gene is present in the genomes of placental and marsupial mammals but not in the platypus, chicken, or fugu genomes.
The green bars in the figure indicate the exons of each gene. The gray bars represent LINEs and SINEs, and the blue bars represent long terminal repeat (LTR) elements of retrotransposons. Solid black diagonal lines link introns, and dashed black lines connect orthologous exons. Arrowheads indicate the direction of transcription.
Using the predicted protein sequence of PEG10, you perform a tblastn search for homologous genes and find that the most similar sequences are in a class of retrotransposons (the sushi-ichi retrotransposons). Propose an evolutionary scenario for the origin of the PEG10 gene, and relate its origin to its biological function.