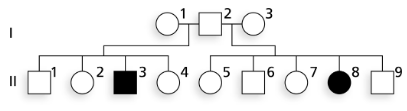
The accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of albinism (absence of skin pigment) in a human family.
Using allelic symbols of your choice, identify the genotypes of the male and his two mates in generation I.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



The accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of albinism (absence of skin pigment) in a human family.
Using allelic symbols of your choice, identify the genotypes of the male and his two mates in generation I.
The accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of albinism (absence of skin pigment) in a human family.
The female I-1 and her mate, male I-2, had four children, one of whom has albinism. What is the probability that they could have had a total of four children with any other outcome except one child with albinism and three with normal pigmentation?
The accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of albinism (absence of skin pigment) in a human family.
What is the probability that female I-3 is a heterozygous carrier of the allele for albinism?
A geneticist crosses a pure-breeding strain of peas producing yellow, wrinkled seeds with one that is pure-breeding for green, round seeds.
Use a Punnett square to predict the F₂ progeny that would be expected if the F₁ are allowed to self-fertilize.
A geneticist crosses a pure-breeding strain of peas producing yellow, wrinkled seeds with one that is pure-breeding for green, round seeds.
What proportion of the F₂ progeny are expected to have yellow seeds? Wrinkled seeds? Green seeds? Round seeds?
A geneticist crosses a pure-breeding strain of peas producing yellow, wrinkled seeds with one that is pure-breeding for green, round seeds.
What is the expected phenotype distribution among the F₂ progeny?