Examine the following diagrams of cells from an organism with diploid number 2n=6, and identify what stage of M phase is represented.

Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
End of meiotic anaphase II
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Diploid and Haploid Numbers

Meiosis

Anaphase II
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
End of mitotic telophase
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
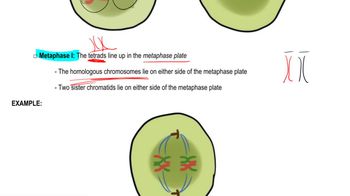
Meiotic metaphase I
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
Early mitotic prophase
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
Mitotic metaphase
Our closest primate relative, the chimpanzee, has a diploid number of 2n = 48. For each of the following stages of M phase, identify the number of chromosomes present in each cell.
Early prophase I
