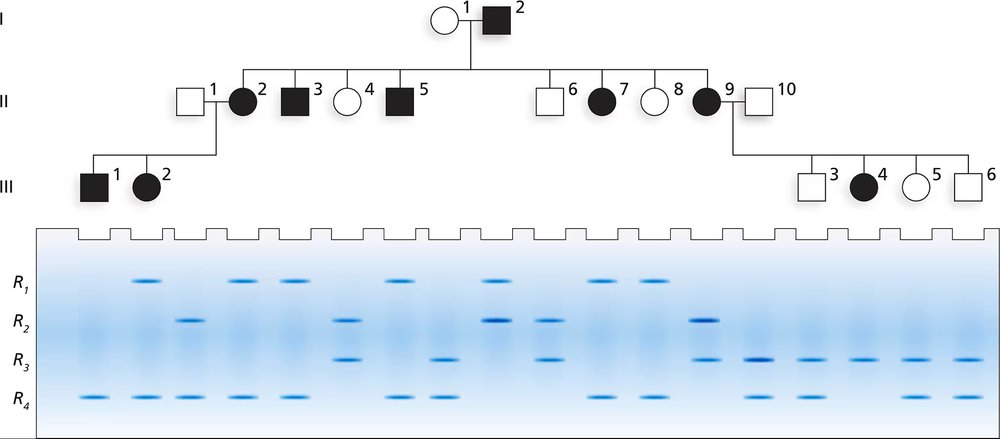
The accompanying pedigree below shows a family in which an autosomal recessive disorder is present. Family members I-2 and II-2 are affected by the disorder and have the genotype dd. A pregnancy involving II-4 has just undergone genetic testing for a VNTR that is linked to the disease gene. The VNTR has a recombination frequency of r = 20 with the disease gene. The VNTR has two alleles, V1 and V2. The gel electrophoresis patterns for each family member are shown, including the VNTR genotype for II-4. Based on the information given, answer the following questions about the family.
What is the chance II-4 has the disease?