The boss in your laboratory has just heard of a proposal by another laboratory that genes for eye color and the length of body bristles may be linked in Drosophila. Your lab has numerous pure-breeding stocks of Drosophila that could be used to verify or refute genetic linkage. In Drosophila, red eyes (c⁺) are dominant to brown eyes (c) and long bristles (d⁺) are dominant to short bristles (d). Your lab boss asks you to design an experiment to test the genetic linkage of eye color and bristle-length genes, and to begin by crossing a pure-breeding line homozygous for red eyes and short bristles to a pure-breeding line that has brown eyes and long bristles.
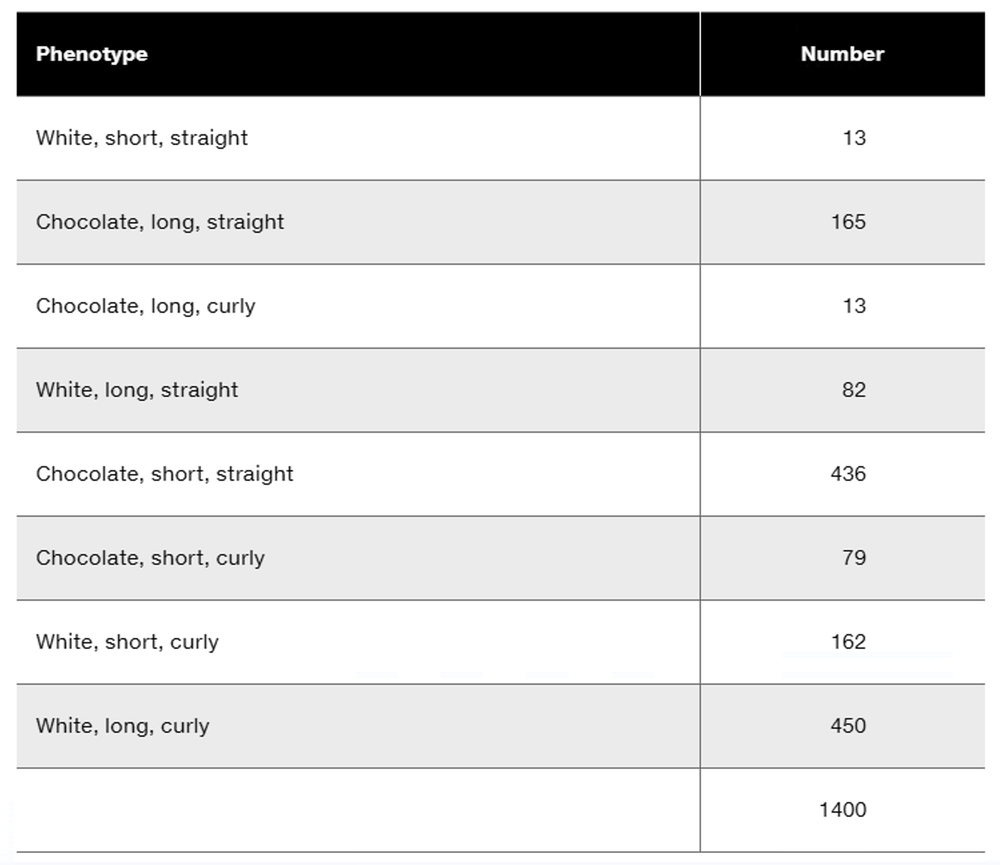
Assume the eye color and bristle-length genes are separated by 28 m.u. What are the approximate frequencies of phenotypes expected from the cross you proposed in part (b)?