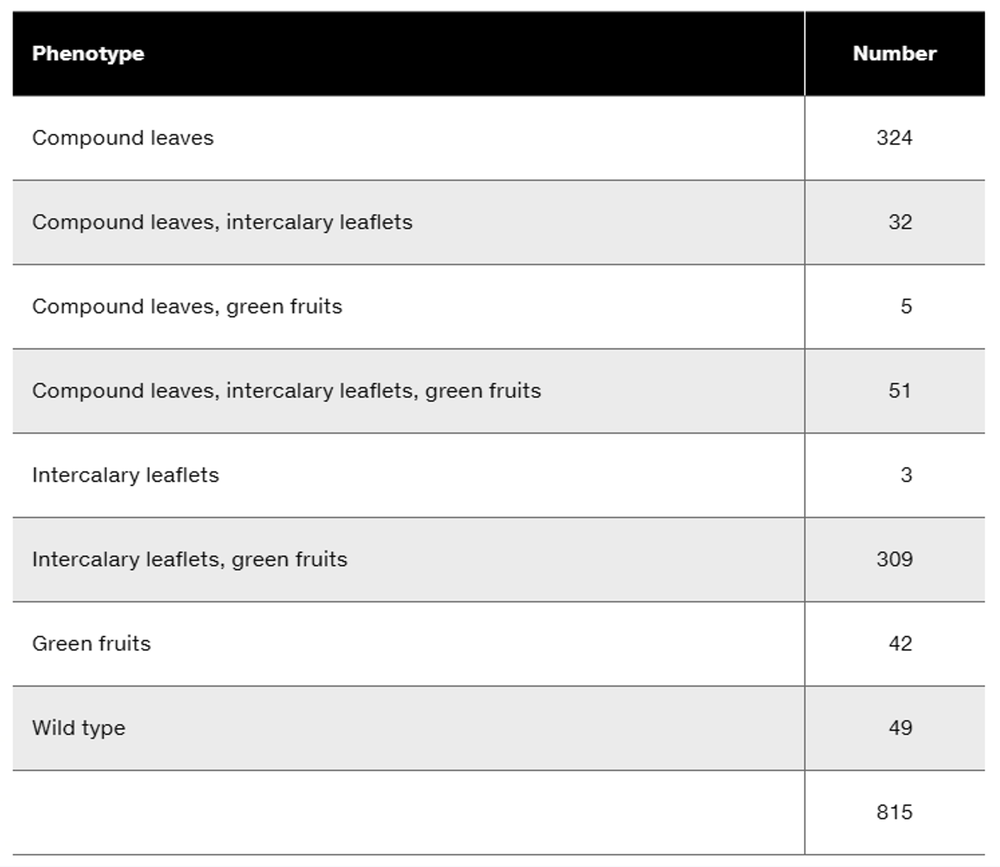
In rabbits, chocolate-colored fur (w⁺) is dominant to white fur (w), straight fur (c⁺) is dominant to curly fur (c), and long ear (s⁺) is dominant to short ear (s). The cross of a trihybrid rabbit with straight, chocolate-colored fur and long ears to a rabbit that has white, curly fur and short ears produces the following results:
Calculate the recombination frequencies between each of the adjacent pairs of genes.