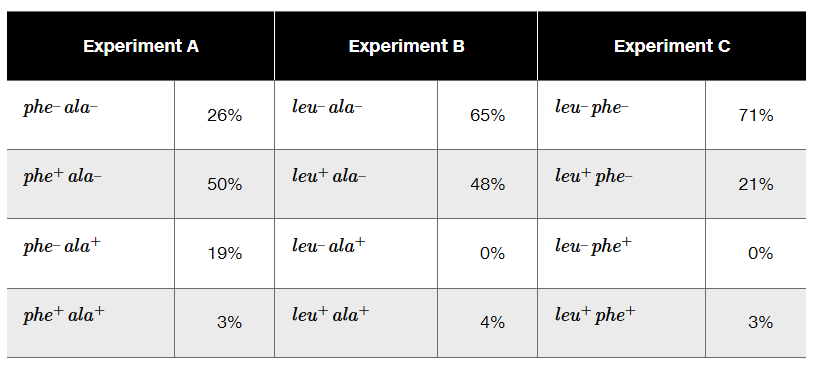
The phage P1 is used as a generalized transducing phage in an experiment combining a donor strain of E. coli of genotype leu⁺ phe⁺ ala⁺ and a recipient strain that is leu⁻ phe⁻ ala⁻. In separate experiments, transductants are selected for leu⁺ (Experiment A), for ala⁺ (Experiment B), and for phe⁺ (Experiment C). Following selection, transductant genotypes for the unselected markers are identified. The selection experiment results below show the frequency of each genotype.
What compound or compounds are added to the minimal medium to select for transductants in Experiments A, B, and C?