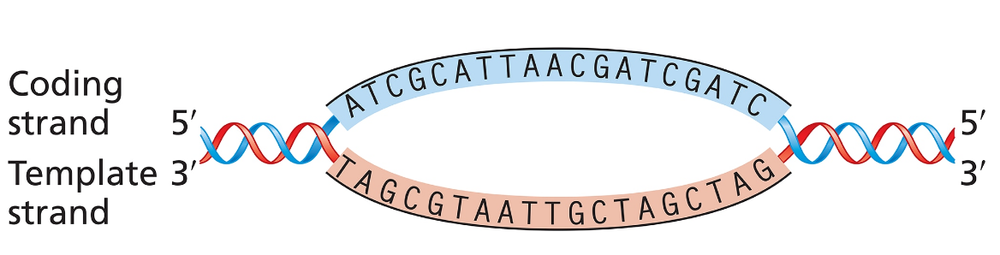
Microbiologists describe the processes of transcription and translation as 'coupled' in bacteria. This term indicates that a bacterial mRNA can be undergoing transcription at the same moment it is also undergoing translation.
How is coupling of transcription and translation possible in bacteria?