Consider translation of the following mRNA sequence:
5′-...AUGCAGAUCCAUGCCUAUUGA...-3′
What events occur to permit the next tRNA to interact with mRNA?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Consider translation of the following mRNA sequence:
5′-...AUGCAGAUCCAUGCCUAUUGA...-3′
What events occur to permit the next tRNA to interact with mRNA?
The diagram of a eukaryotic ribosome shown below contains several errors.
Examine the diagram carefully, and identify each error.
The diagram of a eukaryotic ribosome shown below contains several errors.
Redraw the diagram, and correct each error using the mRNA sequence shown.
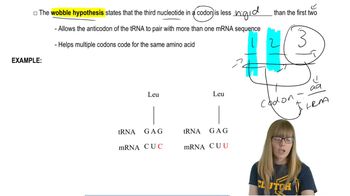
Third-base wobble allows some tRNAs to recognize more than one mRNA codon. Based on this chapter's discussion of wobble, what is the minimal number of tRNA molecules necessary to recognize the following amino acids?
Arginine
Third-base wobble allows some tRNAs to recognize more than one mRNA codon. Based on this chapter's discussion of wobble, what is the minimal number of tRNA molecules necessary to recognize the following amino acids?
Isoleucine
Third-base wobble allows some tRNAs to recognize more than one mRNA codon. Based on this chapter's discussion of wobble, what is the minimal number of tRNA molecules necessary to recognize the following amino acids?
Lysine