Textbook Question
List the type of attractive force disrupted and the level of protein structure changed by the following denaturing treatments:
a. adding salt to soy milk to make tofu
578
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


List the type of attractive force disrupted and the level of protein structure changed by the following denaturing treatments:
a. adding salt to soy milk to make tofu
Identify each of the following statements as characteristic of protein denaturation or protein hydrolysis.
a. Milk curdles when lemon juice is added to it.
Identify each of the following statements as characteristic of protein denaturation or protein hydrolysis.
b. A protein breaks up into amino acid fragments.
What is the name given to the reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
What is the name given to a small, organic nonprotein part of an enzyme that is involved in catalysis?
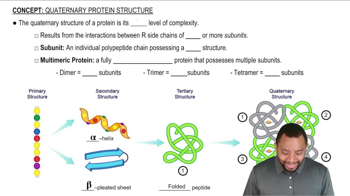
What level of protein structure is involved in the formation of an enzyme’s active site?