The following names are incorrect. What is wrong with each?
a. 1-Pentanone

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



The following names are incorrect. What is wrong with each?
a. 1-Pentanone
The following names are incorrect. What is wrong with each?
b. 2-Butanal
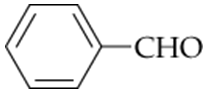
Which of the following compounds will react with Tollens' reagent? With Benedict's reagent?
a. Cyclopentanon
b. Hexanal
c.
Write the structures of the hemiacetal or hemiketal that result from reactions (a) and (b). Write the structures of the complete hydrolysis products of the acetal or ketal in (c) and (d).
a. Acetone + Ethanol → ?
Cyclic hemiacetals commonly form if a molecule has both an alcohol group and a carbonyl group elsewhere in the same molecule, especially if they are four or five carbons apart. What is the structure of the hydroxy aldehyde from which this hemiacetal might form?
What two products result from the complete hydrolysis of this cyclic acetal?