Textbook Question
A compound of gallium with chlorine has a melting point of 77°C and a boiling point of 201°C. Is the compound ionic or covalent? What is a likely formula?
2288
views

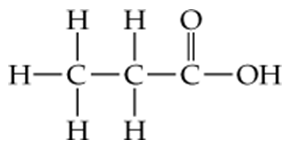
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



A compound of gallium with chlorine has a melting point of 77°C and a boiling point of 201°C. Is the compound ionic or covalent? What is a likely formula?
Distinguish between the following:
b. A structural formula and a condensed structure
Distinguish between the following:
c. A lone pair and a shared pair of electrons
Expand the following condensed structures into the correct structural formulas.
c. CH3CH2OCH2Cl
Draw a Lewis structure for the following molecules:
e. BeCl2 (Note: This molecule does not follow the octet rule.)
Draw a Lewis structure for the following polyatomic ions:
b. Sulfite, SO32–