Textbook Question
Write the base sequence and label the 3' and 5' ends of the complementary strand for a segment of DNA with the following base sequences:
d. 5'CGCGATATTA3'
652
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

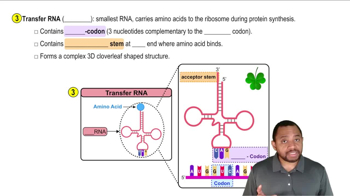

Write the base sequence and label the 3' and 5' ends of the complementary strand for a segment of DNA with the following base sequences:
d. 5'CGCGATATTA3'
Fill in the following table with the analogous nucleic acid structures:
List the similarities and differences in the secondary structure of a protein and the secondary structure of DNA.
List the mRNA bases that complement the bases A, T, G, and C in DNA.
The sequence of bases in a DNA template strand is 5'GGCTTATTGCCA3'. What is the corresponding mRNA produced?
Why are there at least 20 tRNAs?