Provide a reason why there is no vaccine for the common cold.

Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) is a 13-amino-acid peptide hormone responsible for pigmentations in hair and skin. Its peptide sequence is shown.
SYSMQHFRWGKPV
a. How many nucleotides would be found in the mRNA for this protein?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
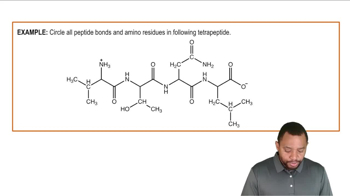
Peptide Hormones
Genetic Code

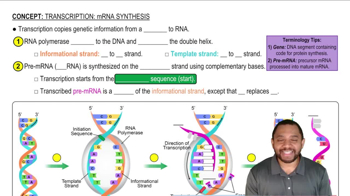
mRNA Synthesis
How is CRISPR different from earlier recombinant DNA techniques?
Oxytocin is a small peptide hormone involved in the process of birthing and lactation. It contains the nine amino acids shown.
CYIQNCPLG
a. How many nucleotides would be found in the mRNA for this protein?
Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) is a 13-amino-acid peptide hormone responsible for pigmentations in hair and skin. Its peptide sequence is shown.
SYSMQHFRWGKPV
b. Suggest an mRNA sequence for the peptide. Show the 5' and 3' ends.
Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) is a 13-amino-acid peptide hormone responsible for pigmentations in hair and skin. Its peptide sequence is shown.
SYSMQHFRWGKPV
c. Suggest a complementary template DNA sequence based on the mRNA sequence suggested in part b.
If the DNA chromosomes of humans contain 20% cytosine, what is the percent of guanine, adenine, and thymine?
