A widely used general anesthetic is called halothane or Fluothane. Its IUPAC name is 2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane. Draw the Lewis structure for this compound.
Ch.4 Introduction to Organic Compounds

Frost4th EditionGeneral, Organic and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134988696Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 1, Problem 64
Draw a condensed structural formula and give the correct IUPAC name for the three alkane structural isomers with the molecular formula C5H12 .
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the molecular formula C_5H_12, which indicates an alkane with 5 carbon atoms and 12 hydrogen atoms.
Recognize that alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with single bonds only, and the general formula for alkanes is C_nH_{2n+2}.
Determine the possible structural isomers by arranging the 5 carbon atoms in different configurations: a straight chain and branched chains.
Draw the condensed structural formulas for each isomer: (1) a straight chain (pentane), (2) a branched chain with a single methyl group (2-methylbutane), and (3) a branched chain with two methyl groups (2,2-dimethylpropane).
Assign the correct IUPAC names to each isomer based on the longest carbon chain and the position of any branches: (1) pentane, (2) 2-methylbutane, and (3) 2,2-dimethylpropane.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkane Structure
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons consisting only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms, connected by single bonds. Their general formula is CnH2n+2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. Understanding the structural arrangement of these atoms is crucial for identifying isomers, which are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural configurations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
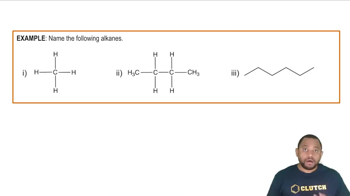
Naming Alkanes Example 1
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of their atoms. For C5H12, there are three distinct structural isomers: n-pentane, isopentane, and neopentane. Recognizing these variations is essential for drawing their condensed structural formulas and naming them correctly according to IUPAC rules.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isomers Concept 1
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides a systematic method for naming chemical compounds. For alkanes, the naming convention is based on the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous chain, with prefixes indicating the number of carbons (e.g., 'pent-' for five). Understanding IUPAC nomenclature is vital for accurately naming the structural isomers of C5H12.
Recommended video:
Guided course

IUPAC Naming Concept 3
Related Practice
Textbook Question
743
views
Textbook Question
The refrigerant 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane has been used in air conditioners in cars since the mid-1990s, but is being phased out due to its environmental impact. Draw the skeletal structure for this compound.
1509
views
Textbook Question
Using condensed structural formulas, draw three conformers of hexane.
1203
views
Textbook Question
How many structural isomers are possible for the molecular formula C5H11F? Draw the skeletal structure and give the IUPAC name of each compound.
709
views
Textbook Question
Using wedge-and-dash bonds, draw a cis and a trans stereoisomers for each of the following compounds:
(b) 1-bromo-2-ethylcyclopentane
567
views
Textbook Question
Using wedge-and-dash bonds, draw both the cis and trans stereoisomers for each of the following compounds:
(b) 1,3-diethylcyclobutane
850
views
