Identify the following reactions as condensation or hydrolysis:
(a) two monosaccharides reacting to form a disaccharide

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

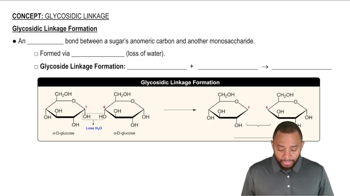

Identify the following reactions as condensation or hydrolysis:
(a) two monosaccharides reacting to form a disaccharide
Name the glycosidic bond present in mannobiose, shown in the following figure:
For each of the following disaccharides, name the glycosidic bond and draw the monosaccharide units produced by hydrolysis:
(a)
Identify a disaccharide that fits each of the following descriptions:
(a) ordinary table sugar
Based on the sweetness index in Table 6.2, if you tasted a drop of each of the syrups below, which would taste the sweetest?
(a) light corn syrup (100% glucose)
If one sweetener packet of Splenda, Sweet’N Low, or Equal has the same sweetness as two tablespoons of sugar, according to Table 6.2, which of the packets contains the smallest amount of the sweetener?