The sugar alcohol erythritol is often included in low-calorie sweeteners. It is 70% as sweet as table sugar. Erythritol is the reduced form of the aldotetrose erythrose. Draw erythritol.
Ch.6 Carbohydrates Life's Sweet Molecules

Frost4th EditionGeneral, Organic and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134988696Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 34
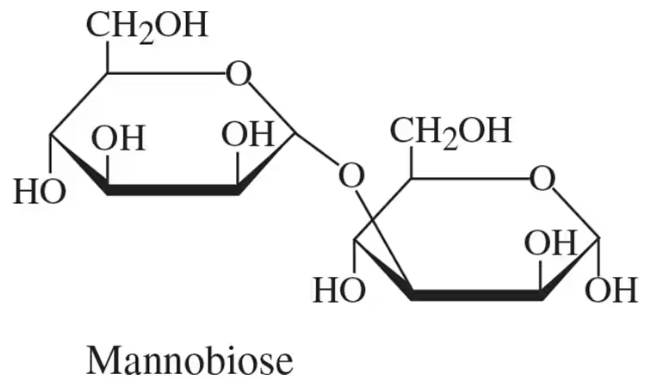
Name the glycosidic bond present in mannobiose, shown in the following figure:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine the structure of mannobiose in the provided image. Identify the two monosaccharide units that make up mannobiose.
Determine the type of glycosidic bond by observing the carbon atoms involved in the linkage. Specifically, look for the carbon number on each monosaccharide that is connected via the oxygen atom.
Check the orientation of the glycosidic bond (alpha or beta) by analyzing the position of the oxygen atom relative to the plane of the monosaccharide rings. If the oxygen is below the plane, it is an alpha bond; if above, it is a beta bond.
Combine the information about the carbon numbers and the orientation to name the glycosidic bond. For example, a bond between C1 of one monosaccharide and C4 of another, with a beta orientation, would be named a β(1→4) glycosidic bond.
Verify the name of the glycosidic bond by cross-referencing with standard carbohydrate nomenclature rules to ensure accuracy.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycosidic Bond
A glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which can be another carbohydrate or a different type of molecule. This bond forms through a dehydration reaction, where a water molecule is released. In disaccharides like mannobiose, the glycosidic bond is crucial for linking two monosaccharides, influencing the structure and properties of the resulting sugar.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Glycosidic Linkage Formation Concept 1
Mannobiose Structure
Mannobiose is a disaccharide composed of two mannose units linked by a glycosidic bond. Understanding its structure is essential for identifying the specific type of glycosidic bond present. The configuration of the bond (alpha or beta) and the position of the linkage (1→2, 1→4, etc.) determine the properties and biological functions of mannobiose.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Structural Formula Concept 2
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are carbohydrates formed by the combination of two monosaccharides through a glycosidic bond. They play significant roles in energy storage and metabolism in living organisms. Mannobiose, as a disaccharide, serves as an example of how simple sugars can combine to form more complex carbohydrates, impacting their digestibility and functionality in biological systems.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Types of Disaccharides Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
640
views
Textbook Question
Pentoses also exist in a ring form, but they most commonly occur as furanose rings. D-Ribose exists in its furanose ring form in the nucleic acid RNA. Using the structure of D-ribose from Table 6.1, draw the furanose form of β-D-ribose.
421
views
Textbook Question
Identify the following reactions as condensation or hydrolysis:
(a) two monosaccharides reacting to form a disaccharide
708
views
Textbook Question
For each of the following disaccharides, name the glycosidic bond and draw the monosaccharide units produced by hydrolysis:
(a)
832
views
Textbook Question
Lactulose is a disaccharide used in the treatment of chronic constipation. Its formal name is galactose β(1→4) fructose.
(a) Draw the structure of lactulose.
696
views
Textbook Question
Identify a disaccharide that fits each of the following descriptions:
(a) ordinary table sugar
617
views
