The sugar alcohol ribitol is a component of the vitamin riboflavin and the energy transfer molecule FAD. Ribitol is formed when the monosaccharide ribose undergoes reduction at carbon 1. Draw the structure of ribitol.

Identify the following reactions as condensation or hydrolysis:
(a) two monosaccharides reacting to form a disaccharide
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
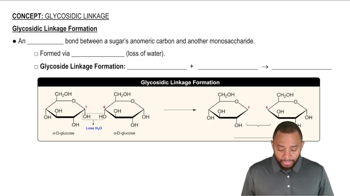
Key Concepts
Condensation Reaction

Hydrolysis Reaction

Glycosidic Bond
The sugar alcohol erythritol is often included in low-calorie sweeteners. It is 70% as sweet as table sugar. Erythritol is the reduced form of the aldotetrose erythrose. Draw erythritol.
Pentoses also exist in a ring form, but they most commonly occur as furanose rings. D-Ribose exists in its furanose ring form in the nucleic acid RNA. Using the structure of D-ribose from Table 6.1, draw the furanose form of β-D-ribose.
Name the glycosidic bond present in mannobiose, shown in the following figure:
For each of the following disaccharides, name the glycosidic bond and draw the monosaccharide units produced by hydrolysis:
(a)
Lactulose is a disaccharide used in the treatment of chronic constipation. Its formal name is galactose β(1→4) fructose.
(a) Draw the structure of lactulose.
