Textbook Question
Rearrange the equation you wrote in Problem 10.50 to solve for [H3O+] in terms of Ka.
1168
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


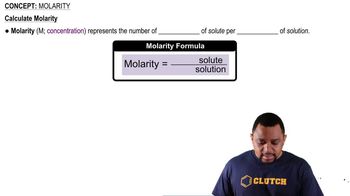
Rearrange the equation you wrote in Problem 10.50 to solve for [H3O+] in terms of Ka.
The pH of a buffer solution containing 0.10 M acetic acid and 0.10 M sodium acetate is 4.74.
a. Write the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation for this buffer.
How does normality compare to molarity for monoprotic and polyprotic acids?
How many equivalents of an acid or base are in the following?
a. 0.25 mol Mg(OH)2
What are the molarity and the normality of a solution made by dissolving 5.0 g of Ca(OH)2 in enough water to make 500.0 mL of solution?
What are the molarity and the normality of a solution made by dissolving 25 g of citric acid (triprotic, C6H5O7H3) in enough water to make 800 mL of solution?