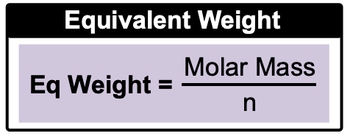
In the study of acids and bases, the concept of equivalents is crucial for understanding their reactivity and neutralization. An equivalent of an acid is defined as the amount of acid that can donate one mole of hydrogen ions (H+), while an equivalent of a base is the amount that can provide one mole of hydroxide ions (OH-). This relationship allows chemists to quantify the strength and capacity of acids and bases in reactions.
For instance, consider hydrobromic acid (HBr). One mole of HBr yields one mole of H+ ions, thus it is equivalent to one equivalent of acid. In contrast, calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) contains two hydroxide ions per formula unit. Therefore, one mole of calcium hydroxide corresponds to two equivalents, as it can donate two moles of OH- ions.
Understanding the concept of equivalents becomes particularly important when dealing with reactions involving different amounts of acids and bases. The varying number of equivalents can influence the outcome of neutralization reactions, where the stoichiometry of the reactants determines the final products. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for deeper exploration into acid-base chemistry and the calculations involved in titrations and other analytical methods.