Textbook Question
Name the following compounds:
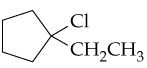
a.
b.
1004
views

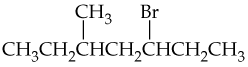
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Name the following compounds:
a.
b.
Name the following compounds:
a.
b.
c.
What disulfides would you obtain from oxidation of the following thiols?
a. CH3CH2CH2SH
b. 3-Methyl-1-butanethiol (skunk scent)
2-Aminopropane is an achiral molecule, but 2-aminobutane is chiral. Explain.
Which of the following molecules are chiral? (Hint: Draw each molecule and analyze it as illustrated in Worked Example 14.2.)
a. 3-Chloropentane
b. 2-Chloropentane
c.
Predict the product of the following reaction:
<IMAGE>