Textbook Question
From what alcohols might the following carbonyl-containing products have been made (red = O, reddish-brown = Br)?
(a) <IMAGE>
(b) <IMAGE>
650
views

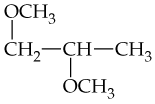
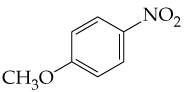
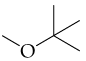
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



From what alcohols might the following carbonyl-containing products have been made (red = O, reddish-brown = Br)?
(a) <IMAGE>
(b) <IMAGE>
Draw structures for the following:
a. 2,4-Dinitrophenol
b. m-Ethylphenol
Name the following compounds:
a.
b.
What disulfides would you obtain from oxidation of the following thiols?
a. CH3CH2CH2SH
b. 3-Methyl-1-butanethiol (skunk scent)
Give systematic names for the following alkyl halides:
a.
b.
2-Aminopropane is an achiral molecule, but 2-aminobutane is chiral. Explain.