Can the alcohol (CH3)3COH be formed by the reduction of an aldehyde or ketone? Why or why not?
Ch.15 Aldehydes and Ketones

Chapter 15, Problem 61
The liquids 1-butanol and butanal have similar molar masses. Which is expected to have the higher boiling point? Explain your choices.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the functional groups present in 1-butanol and butanal. 1-butanol contains a hydroxyl (-OH) group, making it an alcohol, while butanal contains a carbonyl (C=O) group, making it an aldehyde.
Understand the intermolecular forces present in each compound. Alcohols like 1-butanol can form hydrogen bonds due to the -OH group, while aldehydes like butanal primarily exhibit dipole-dipole interactions and London dispersion forces.
Recall that hydrogen bonding is a stronger intermolecular force compared to dipole-dipole interactions and London dispersion forces. This means that substances capable of hydrogen bonding generally have higher boiling points.
Consider the molecular structure and size. Since both 1-butanol and butanal have similar molar masses, the difference in boiling points will primarily depend on the strength of their intermolecular forces rather than their size or mass.
Conclude that 1-butanol is expected to have a higher boiling point than butanal because the hydrogen bonding in 1-butanol requires more energy to overcome compared to the dipole-dipole interactions in butanal.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces between molecules that influence physical properties like boiling points. Stronger intermolecular forces typically lead to higher boiling points. In the case of 1-butanol and butanal, the presence of hydrogen bonding in 1-butanol, due to its hydroxyl (-OH) group, contributes to stronger intermolecular attractions compared to the dipole-dipole interactions in butanal.
Recommended video:
Guided course
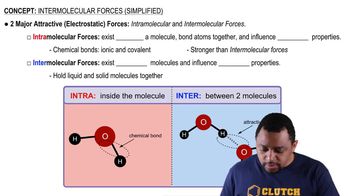
Intermolecular Forces (Simplified) Concept 1
Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the external pressure, allowing it to transition from liquid to gas. Factors affecting boiling points include molecular weight, structure, and intermolecular forces. In comparing 1-butanol and butanal, the boiling point can be predicted based on the types of intermolecular forces present in each compound.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Boiling Point Elevation Concept 1
Molecular Structure
Molecular structure refers to the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, which affects its physical and chemical properties. 1-butanol has a straight-chain structure with a hydroxyl group, while butanal is an aldehyde with a carbonyl group. This structural difference influences the types of intermolecular forces present, ultimately affecting their boiling points.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Models Example 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
811
views
Textbook Question
Many flavorings and perfumes are partially based on fragrant ketones, with far fewer being based on fragrant aldehydes. Why do you think ketones are used more frequently than aldehydes? See Section 15.5 for a clue.
38
views
Textbook Question
Draw the structural formulas of the following compounds:
c. 2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
1361
views
Textbook Question
Draw all the ketones you can with a chemical formula of C8H16O whose longest chain is eight carbons. Name each using both its IUPAC and common name.
869
views
Textbook Question
In Problem 15.24, you were given the structure of the free aldehyde form of glucose. Try to draw the two cyclic hemiacetal forms of glucose you would get if (a) the OH on C4 formed the ring and (b) the OH on C3 formed the ring.
759
views
