In its open-chain form, D-mannose, an aldohexose found in orange peels, has the structure shown here. Coil mannose around and draw it in the cyclic hemiacetal ⍺ and β forms.

Treatment of an aldose with an oxidizing agent such as Tollens’ reagent yields a carboxylic acid. Gluconic acid, the product of glucose oxidation, is used as its magnesium salt for the treatment of magnesium deficiency. Draw the structure of gluconic acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Aldose

Oxidizing Agents
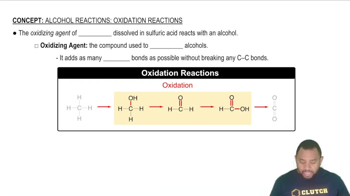
Gluconic Acid
Treatment of D-glucose with a reducing agent yields sorbitol, a substance used as a sugar substitute by people with diabetes. Draw the structure of sorbitol.
Reduction of D-fructose with a reducing agent yields a mixture of D-sorbitol along with a second, isomeric product. What is the structure of the second product?
Oxidation of the aldehyde group of ribose yields a carboxylic acid. Draw the structure of ribonic acid.
Look at the open-chain form of D-mannose and draw the two glycosidic products that you expect to obtain by reacting D-mannose with methanol.
Draw a disaccharide of two cyclic mannose molecules attached by an α-1,4 glycosidic linkage. Explain why the glycosidic products in Problem 20.58 are not reducing sugars, but the product in this problem is a reducing sugar.
