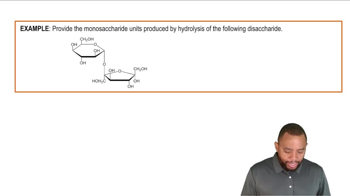
Textbook Question
What two coenzymes are involved with initial events of the electron-transport chain?
1483
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

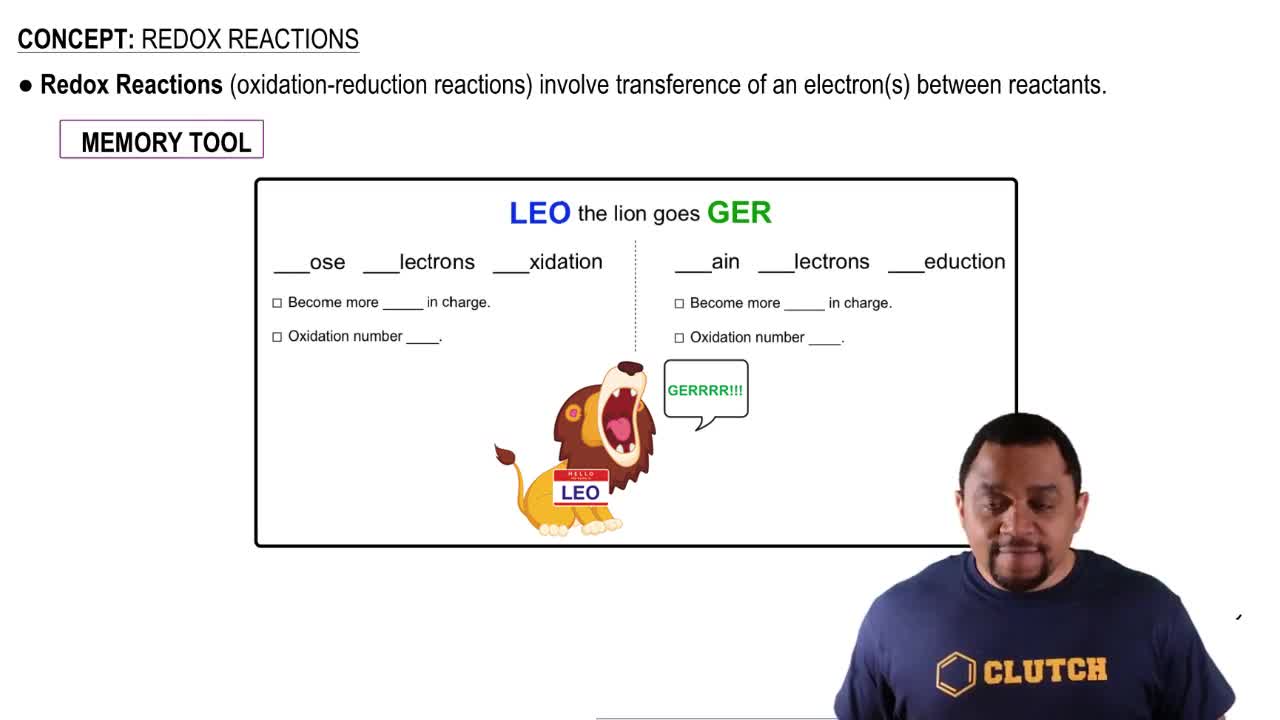
What two coenzymes are involved with initial events of the electron-transport chain?
What are the ultimate products of the electron-transport chain?
What do the following abbreviations stand for?
b. CoQ
What atom in the cytochromes undergoes oxidation and reduction in the electron-transport chain? What atoms in coenzyme Q undergo oxidation and reduction in the electron-transport chain?
What would happen to the citric acid cycle if NADH and FADH2 were not reoxidized?
What does the term “oxidative phosphorylation” mean? What is substrate-level phosphorylation? Are these processes the same? Explain.