Use curved arrows (like those in Figure 22.3) to write an equation for the conversion of fructose to fructose 6-phosphate by ATP. At what step does fructose 6-phosphate enter glycolysis?

Glycolysis of one molecule of glucose produces 8 ATP molecules. How many ATP molecules are produced from glycolysis of 10 glucose molecules?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
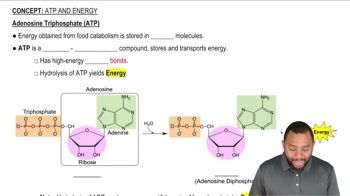
Key Concepts
Glycolysis

ATP Production
Stoichiometry in Biochemical Reactions

In alcoholic fermentation, each mole of pyruvate is converted to one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of ethanol. In the process, about 50 kcal/mol (209 kJ/mol) of energy is produced. Under the most favorable conditions, more than one-half of this energy is stored as ATP.
a. What happens to the remaining energy produced in alcoholic fermentation?
Pyruvate has three different fates. What are the three different molecules pyruvate is converted into? What conditions exist for the formation of each product?
What two types of reactions convert glycerol to dihydroxyacetone phosphate?
What is the purpose of the Cori cycle?
Glucose 6-phosphate is in a pivotal position in metabolism. Depending on conditions, glucose 6-phosphate follows one of several pathways. Under what conditions do the following occur?
b. Hydrolysis to free glucose
