Write an equation for the complete hydrogenation of triolein, the triacylglycerol with three oleic acid acyl groups for which you drew the structure in Problem 23.3. Name the fatty acid from which the resulting acyl groups are derived.

Identify the products formed by complete hydrolysis of all ester bonds in (b) the sphingomyelin in Figure 23.5.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
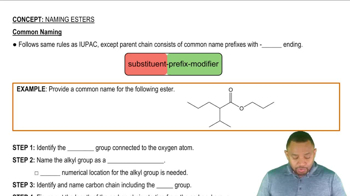
Key Concepts
Ester Bonds
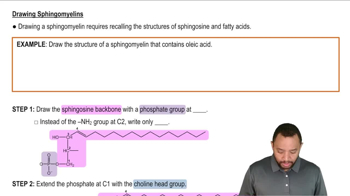
Sphingomyelin
Complete Hydrolysis

Write the complete equation for the hydrolysis of a triacylglycerol in which the fatty acids are two molecules of stearic acid and one of oleic acid.
Identify the products formed by complete hydrolysis of all ester bonds in (a) the phosphatidylcholine on page 726.
Draw the structure of the sphingomyelin that contains a myristic acid acyl group. Identify the hydrophilic head group and the hydrophobic tails in this molecule.
Draw the structure of the glycerophospholipid that contains a stearic acid acyl group, an oleic acid acyl group, and a phosphate bonded to ethanolamine.
Which of the following terms apply to the compound shown below? (Hint: Look at the functional groups and the bonds involved to begin analyzing the compound part by part in comparison to the lipids discussed in this chapter.)
a. A phospholipid
