Textbook Question
Write the equation for the final step in the catabolism of any fatty acid with an even number of carbons.
651
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


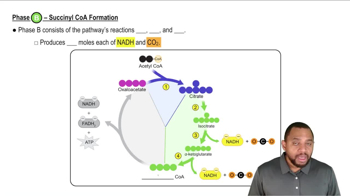
Write the equation for the final step in the catabolism of any fatty acid with an even number of carbons.
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA result from complete catabolism of the following compounds?
a. Myristic acid, CH3(CH2)12COOH
What causes acetone to be present in the breath of someone with uncontrolled diabetes?
How many rounds of the lipogenesis cycle are needed to synthesize stearic acid, C17H35COOH?
Consuming too many carbohydrates causes deposition of fats in adipose tissue. How does this happen?
Why are extra calories consumed as carbohydrates stored as fat and not as glycogen?