Back
BackProblem 1
In developed nations, which of the following are considered endemic diseases, and which are considered sporadic diseases?
Influenza: (endemic or sporadic)
Tetanus: (endemic or sporadic)
Plague: (endemic or sporadic)
Common cold: (endemic or sporadic)
Streptococcal pharyngitis: (endemic or sporadic)
Botulism: (endemic or sporadic)
Pneumonia: (endemic or sporadic)
Problem 2
Indicate the true statements and then correct the false statements, so they are true.
a. Zoonotic diseases pass from humans to animals.
b. Communicable diseases spread from person to person.
c. Noncommunicable diseases are contagious.
d. Koch’s postulates of disease are mainly used to study noninfectious diseases.
Problem 3
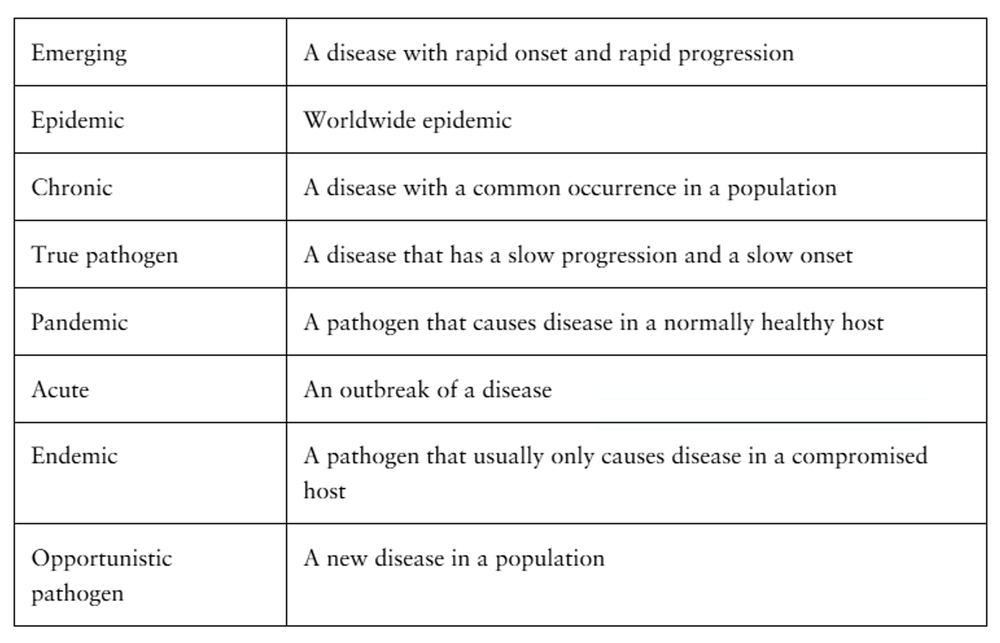
Match the following:
Problem 4
List three functions of public health.
Problem 5
State what type of mortality rate is applicable.
Scenario 1: Out of 6,000 live births last week, 10 of the women died.
Type of mortality rate?
Scenario 2: 300 patients had disease X last year, 10 of whom died.
Type of mortality rate?
Scenario 3: Of the 120,000 live births in a particular community last year, 15 of the babies died before their first birthday.
Type of mortality rate?
Scenario 4: Out of 3,000 people in a given population, 100 died of pneumonia.
Type of mortality rate?
Calculated mortality rate (expressed per 100 in the population):
Problem 6
Draft a Venn diagram to compare and contrast descriptive and analytical epidemiology.
Problem 7
Diseases that the CDC collects information on through collaboration with state and local health authorities are called (NCLEX/HESI/TEAS)
a. Communicable diseases.
b. Reportable diseases.
c. Nationally notifiable diseases.
d. Investigative diseases.
e. Case report illnesses.
Problem 8
An epidemiological study design that is commonly used for determining the efficacy of a drug therapy is a(n)
a. Experimental study.
b. Case report.
c. Cross-sectional study.
d. Correlation study.
e. Observational study.
Problem 9
A(n) _______________________ groups the study populations by exposure versus nonexposure to a certain risk factor to see if either group develops the outcome in question.
a. Experimental study
b. Case report
c. Cross-sectional study
d. Correlation study
e. Observational study
Problem 10
Label the following modes of transmission as either direct or indirect. For all indirect transmissions, also specify which of the three categories of indirect transmission is involved.
Transmission of HIV across the placenta:
Transmission of a pathogen through drinking contaminated water:
Transmission of malaria by a mosquito to a human host:
Transmission of a pathogen through breast milk:
Transmission of rabies by a dog bite:
Transmission of a pathogen by touching a doorknob:
Transmission of a pathogen by a contaminated needle:
Transmission of a respiratory pathogen through respiratory droplets:
Problem 11
From the following choices, select all of the factors that impact prevalence rate.
a. Duration of a disease
b. The type of pathogen responsible (such as if the pathogen is viral or bacterial)
c. Cure rates for a disease
d. The pathogenicity of the microbe that causes the disease
e. The effectiveness of preventive measures
f. The incidence rate of a disease
g. The quality of diagnostic tools
h. The severity of the disease