Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates the endosymbiotic hypothesis.
<IMAGE>

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
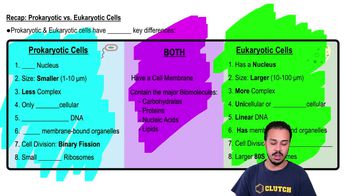


Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates the endosymbiotic hypothesis.
<IMAGE>
Which of the following kingdoms or domains is a hodgepodge of different evolutionary lineages?
a. Bacteria
b. Protista
c. Archaea
d. Plantae
e. Animalia
Comparisons of ribosomal RNA among many different modern species indicate that
a. There are two very divergent groups of prokaryotes
b. The Protista represents a conglomeration of very unrelated forms
c. Fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants
d. A and B are correct
e. A, B, and C are correct
The mitochondria in a eukaryotic cell
a. Serve as the cell's power plants
b. Probably evolved from a prokaryotic ancestor
c. Can live independently of the eukaryotic cell
d. A and B are correct
e. A, B, and C are correct
Fungi feed by
a. Producing their own food with the help of sunlight
b. Chasing and capturing other living organisms
c. Growing on their food source and secreting chemicals to break it down
d. Filtering bacteria out of their surroundings
e. Producing spores
Which of the following is/are always true?
a. Viruses cannot reproduce outside a host cell
b. Viruses are not surrounded by a membrane
c. Viruses are not made up of cells
d. A and C are correct
e. A, B, and C are correct