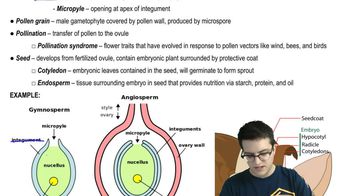
Double fertilization means that:
a. Flowers must be pollinated twice to yield fruits and seeds
b. Every egg must receive two sperm to produce an embryo
c. One sperm is needed to fertilize the egg, and a second sperm is needed to fertilize the polar nuclei
d. Every sperm has two nuclei