Textbook Question
What volume of 0.200 M ethanol solution contains each amount in moles of ethanol? b. 1.22 mol ethanol
496
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
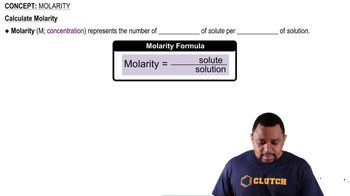


What volume of 0.200 M ethanol solution contains each amount in moles of ethanol? b. 1.22 mol ethanol
What volume of 0.200 M ethanol solution contains each amount in moles of ethanol? c. 1.2⨉10-2 mol ethanol
A laboratory procedure calls for making 400.0 mL of a 1.1 M NaNO3 solution. What mass of NaNO3 (in g) is needed?
If 123 mL of a 1.1 M glucose solution is diluted to 500.0 mL, what is the molarity of the diluted solution?
If 3.5 L of a 4.8 M SrCl2 solution is diluted to 45 L, what is the molarity of the diluted solution?
To what volume should you dilute 50.0 mL of a 12 M stock HNO3 solution to obtain a 0.100 M HNO3 solution?