Cat breeders are aware that kittens expressing the X-linked calico coat pattern and tortoiseshell pattern are almost invariably females. Why are they certain of this?

Define the Lyon hypothesis.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
X-Chromosome Inactivation

Lyon Hypothesis
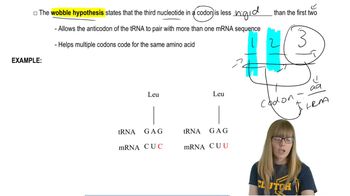
Dosage Compensation

It has been suggested that any male-determining genes contained on the Y chromosome in humans cannot be located in the limited region that synapses with the X chromosome during meiosis. What might be the outcome if such genes were located in this region?
What is a Barr body, and where is it found in a cell?
Indicate the expected number of Barr bodies in interphase cells of individuals with Klinefelter syndrome, Turner syndrome, and karyotypes 47, XYY, 47, XXX, and 48, XXXX.
Can the Lyon hypothesis be tested in a human female who is homozygous for one allele of the X-linked G6PD gene? Why, or why not?
Predict the potential effect of the Lyon hypothesis on the retina of a human female heterozygous for the X-linked red-green color blindness trait.
